Maine Nightjar Monitoring
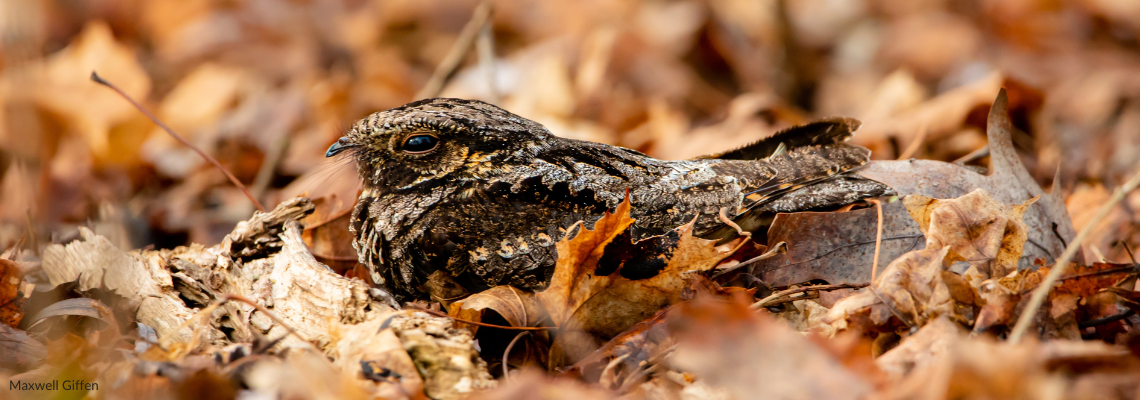

Tracking the Migration Route of Maine Whip-poor-wills
Maine’s aerial insectivores (swallows, whip-poor-wills, nighthawks, and more) are in trouble. Although many of us grew up hearing Eastern Whip-poor-wills calling in meadows and blueberry barrens, their population has declined 69% in Eastern North America since 1970. Very little is known about the ecology of whip-poor-wills in Maine and the factors causing their decline. As Maine adjusts to a changing climate, it is vitally important that biologists and policymakers have access to baseline data on Maine whip-poor-wills so they know how to protect them in the future.
To address this need, the Observatory is expanding its Maine Nightjar Monitoring project to:
- Identify threats to the breeding success of whip-poor-wills and assess changes in habitat.
- Conduct DNA barcoding of fecal samples to see what Maine whip-poor-wills are eating.
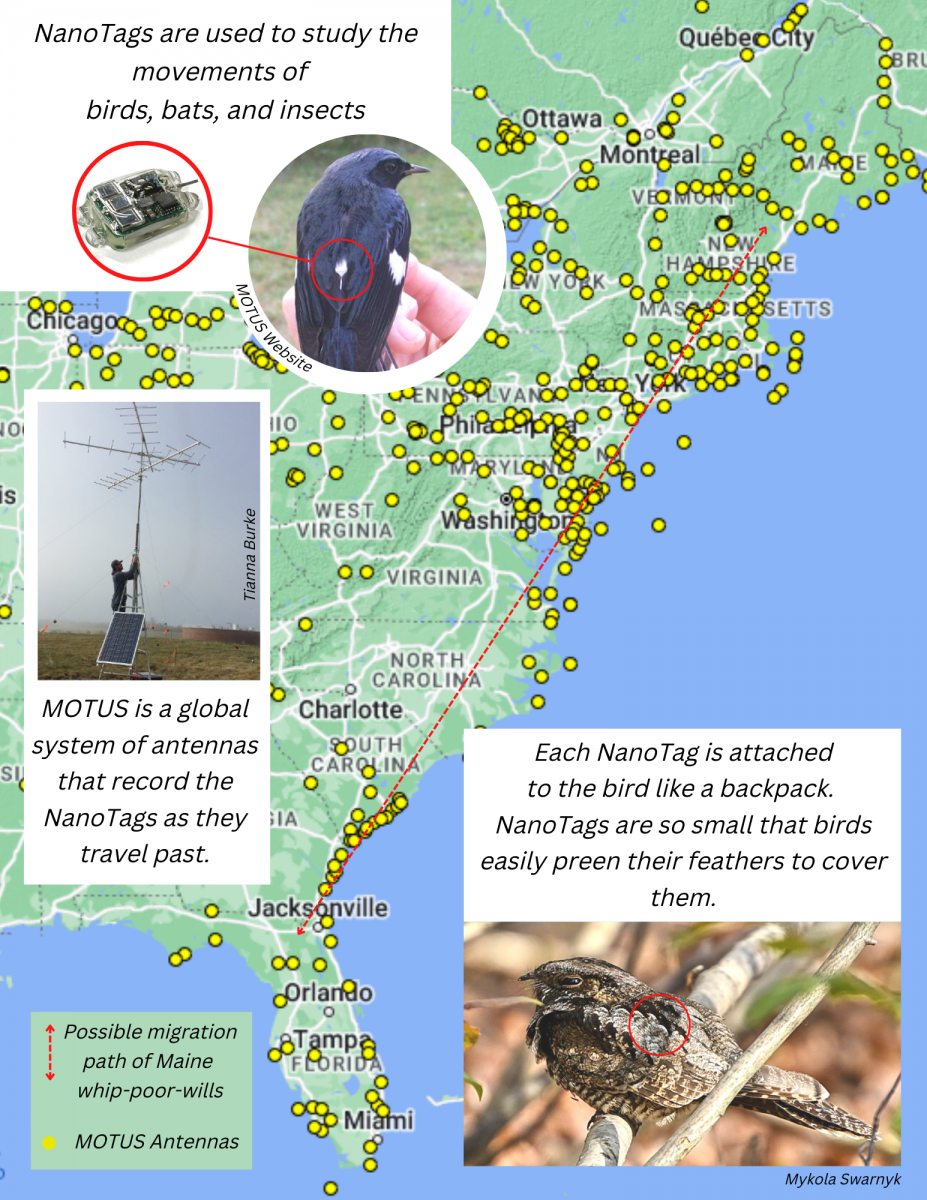
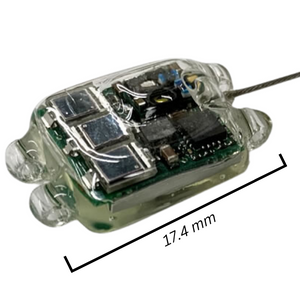
- Track the migratory path of Maine whip-poor-wills using state-of-the-art, solar-powered NanoTags attached to the bird like a backpack.
Check out the project's Motus site to see which antennas
have detected our whip-poor-wills so far
Why Eastern Whip-poor-wills?
The rate of decline in Maine whip-poor-wills is currently unknown although anecdotal evidence suggests that their decline is significant. The cause of this decline is also unknown although predation on breeding grounds, declining insect populations, and challenges in migration are all suspected.
Volunteer With The Project
We are currently seeking volunteers to conduct nightjar surveys along predetermined routes throughout the state. Visit the project website to select a route and to sign up as a project volunteer.
About The Maine Nightjar Monitoring Project
The Maine Nightjar Monitoring Project was launched in 2017 to monitor Maine's two Nightjar species: the Eastern Whip-poor-will and the Common Nighthawk. Both of these species are experiencing significant declines throughout their breeding ranges and anecdotal reports have also indicated declines here in Maine.
Each year, volunteers conduct surveys along routes through nightjar habitat. Surveys are conducted at dusk and again on moonlit nights. In addition to nightjars, volunteers collect observations of owls, thrushes, and other crepuscular (twilight) and nocturnal birds. The data from this project will be used to inform the management of these species here in Maine.
LEARN MORE: Maine Nightjar Monitoring Project
Nightjar monitoring training video
Get Involved
Want to help us monitor Eastern Whip-poor-wills and other nightjars? We need motivated citizen scientists to help with this project! Contact logan@mainenaturalhistory.org for more information on how to get involved.
Stay Connected
Want to follow the progress of the Maine Nightjar Monitoring Project? Even if you aren’t able to give a gift today, liking and following the Observatory on Facebook and Instagram helps us reach more people. Thank you!
Resources












